Layout¶
The Layout Component takes care of Positioning & Alignment of elements whitin a Screen.
Layout Properties¶
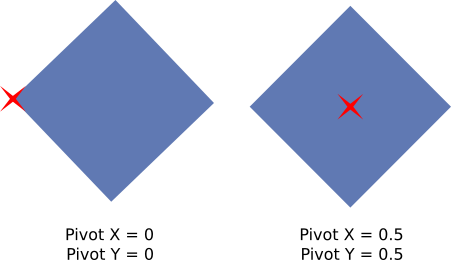
Pivot¶
The Pivot is the center of transformation of 2D elements.
Positioning, Alignment, Rotation, and Scaling are all done with respect to the pivot.
The X and Y components of the Pivot are in normalized 2D element space (between 0 and 1).
Rotation¶
Rotates in degrees around the Pivot. Examples with a 45 degrees rotation:
Note
Although Rotation is a 3 dimensional Vector, the Z component is what you typically need to rotate 2D elements
Scaling¶
Scales the element around the Pivot
Offset¶
Moves the element relative to the Pivot
Horizontal Alignment¶
Horizontally aligns an element relative to its parent, using the Pivot’s X component as an anchor.
Left Alignment
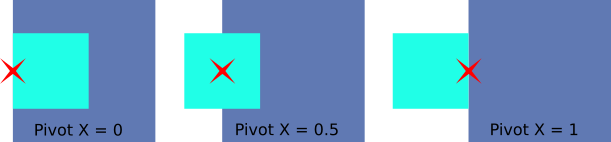
Center Alignment

Right Alignment

Stretch Mode: The element stretches horizontally to fit the parent. The Pivot’s X component is ignored in this case.

Vertical Alignment¶
Vertically aligns an elements relative to its parent, using the Pivot’s Y component as an anchor.
Top Alignment
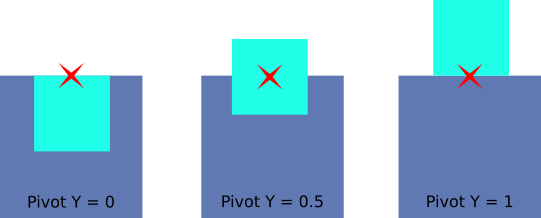
Center Alignment

Bottom Alignment
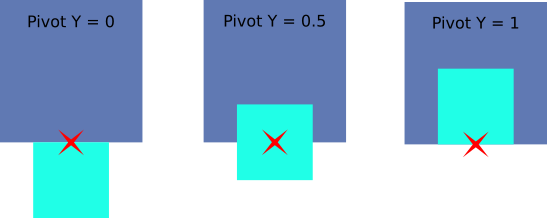
Stretch Mode: The element stretches vertically to fit the parent. The Pivot’s Y component is ignored in this case.
Width¶
Auto: The width is determined based on the content of the element. This is typically the width of the main texture used by the element.
Relative: The width is a percentage, relative to the parent Element.
Absolute: The width is in pixels, in virtual Screen space.
Height¶
Auto: The height is determined based on the content of the element. This is typically the height of the main texture used by the element.
Relative: The height is a percentage, relative to the parent Element.
Absolute: The height is in pixels, in virtual Screen space.
Margin¶
This defines Left, Right, Top, and Bottom spacing around the element, in the same fashion as CSS Margins.
Tint¶
Layout Tint is useful to globally affect the color of a hierarchy of elements.
It propagates down the hierarchy in a multiplicative way.
A typical usage is to fade entire parts of the UI.
Inherit Tint¶
Defines whether an Element takes its parent’s Tint into account.